Surviving in today’s world without the internet is impossible, especially if you are running a business. The Internet allows the connected devices to communicate across the globe using an Internet protocol. The better the protocol, the better connection you will have. There are two major internet protocols: IPv4 vs IPv6. For decades, the internet has been using the IPV4 that is based on a numerical address. However, as the IT sector advanced, there was an unprecedented growth in data transfer units. The increasing data load creates the demand for a better protocol that can handle improved capacities and facilitate better data exchange. That’s how IPV4 came into existence. In this blog, we will carry out a detailed analysis of IPV4 vs IPV6, and explain the difference between ipv4 and ipv6.
What is an IP address?
An Internet Protocol address is a unique number given to each connected device by the main Internet router. This allows devices on the network to communicate with all other devices. There are two types of IP addresses: public and private IP addresses. Private IP addresses are assigned by router DHCP and work only inside a local area network. On the other hand, public IP addresses are globally unique and are provided by Internet service providers. Generally, all everyday devices, like laptops, phones, etc., are connected to the LAN. while your main router has a public IP address.
What is IPv4?
IPv4 has been the foundational Internet protocol that has helped the exchange of information for over several decades. IPv4 is the fourth version of the internet protocol. Internet protocol is the set of rules that are used to communicate between devices across the globe. The IPV4 provides a unique numerical address that is known as an IP address that allows different devices to connect with each other on the worldwide cloud.
IPv4 Address Format
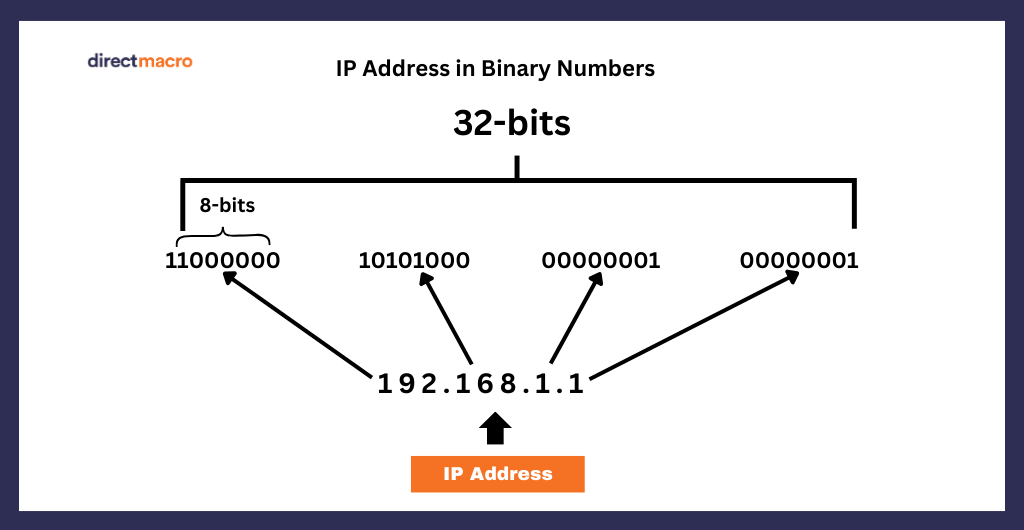
IPv4 is a 32-bit address format that is expressed in decimal notation; for instance, 192.168.1.1 can be an IP address. It has a group of four sections, which can have varying integers, separated with decimals. These sections are called octets or bytes. The number code address is given to each device that connects with the other device over the internet. The 32-bit IPv4 format, considering the (2)32, the number of ipv4 addresses forms are more than 4 billion.
The IPV4 address is then converted into the binary number; here is how each octet is converted into the binary number.
The four sets of binary numbers, each denoting 8 bits, make a 32-bits IP address. here is the explanations:
What is IPv6?
IPv6 is right now the most used Internet protocol version. IPv6 was designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force in 1998. ARIN and World IPv6 were finally launched in 2012.
When the IPV4 global supply became exhausted, the internet protocol transitioned to a better version that can handle the shortcomings of the previous version and offer complete support in all ways possible. Although IPv6 too is not free from challenges. It began a new wave of internet and global interconnectivity of devices. It offers a bigger address space, better security, and faster speed than the previous protocol, IPV4.

IPv6 Address Format
Unlike IPV4, an IPV6 address consists of 128 bits that are grouped in 8 sets of four-digit numbers. It offers much bigger space compared to IPv4. It can include both letters and numbers in the address. Each group is 16 bits and consists of four hexadecimal digits from 0 to 9 and later A-F. Each group is separated by a colon (:).
An example of the IPV6 address format is here:
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
The first 3 sets of 4 digits are Network Prefix; the next 2 groups of sets are Subnet ID. The last three sets of digits are called the network identifier. However, this 32-digit IP address can be shortened. You can omit the subnet ID from this. You can remove the consecutive groups of zeros and replace them from the (::). However, remember that you can only do it once in an IP address.
Full IPV6 IP Address: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
Shorten IP Address: 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334
Difference between IPV4 and IPV6
Wondering what is IPv6 vs IPv4? The chart below shows the differences between the features of ipv4 and ipv6.
| IPV6 | IPV4 |
| IPv6 offers a 128-bit address, offering four times greater space than IPv4. | IPV4 offers a 32-bit address, offering about 4 million unique IP addresses. |
| An IPV6 address includes a combination of numbers and letters. | It includes groups of integers that are separated into sections using decimals. |
| IPv6 supports network traffic from unicast, multicast, and anycast networks. | IPv4 supports network traffic unicast, broadcast, and anycast networks. |
| It has no built-in security feature, and security depends on the application. | It has IPSE’s built-in security features and needs no external support. |
| IPV6 offers the data packet flow identification, that improve network efficiency and quality of service. | IPV4 does not provide packet flow identification, that often affect connection performance in heavy workload. |
| IPV removes the header checksum to improve efficiency; however, it relies on lower- and upper-layer error detection mechanisms. | Checksum and Cyclic Redundancy are the two main network error detections IPV4 has. |
| IPv6 does not have backward compatibility. You cannot convert all IPV6 addresses to IPV4 addresses. | Valid IPV4 addresses can be easily converted into IPV6 addresses. |
How to Check If You’re Using IPv4 or IPv6?
Curious about which internet protocol you are using? You can simply check by the window command prompt. Here is the process:
Press the Window button and R-key simultaneously.
Type “cmd” here. Click “OK” You will find a command box like that.
On top of the box, you will find IP address.
If your IP address starts with 192.168.x.x, you have an Internet Protocol version 4. If you have an IP address such as fe80::, you have IPV6. On the other hand, IPV4 can be a private IP address if starts with something like 10.x.x.x and 192.168.x.x. The range of this private IP starts from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255.
| Private IPV4 | Range Starts | Range Ends |
| 16- Bit block | 192.168.0.0 | 192.168.255.255 |
| 20- Bit block | 172.16.0.0 | 172.31.255.255 |
| 24- bit block | 10.0.0.0 | 10.255.255.255 |
How to Switch from IPV4 to IPv6?
If you want to switch from IPV4 to IPV6, you have to be sure that you have a valid IPV4. Make sure ISP, router, and device supports IPV6. Here is how to change ipv4 to ipv6.
- Go to any online IPv4 to IPv6 Converter.
- Enter your IPV4 address.
- Proceed ahead with the button saying convert to IPV4 to IPV6.
- The tool will give you all versions of compressed and expanded IPV6 addresses.
Conclusion
This blog carries out a fair analysis of IPV4 vs IPV6. After carefully evaluating both protocols, we reach the conclusion that IPV6 is better than IPV4. IPV4 is a bit older internet protocol, while IPV6 incorporates the latest protocol technology that comes with a greater capacity to handle large data flow. While both Internet protocols have their strengths and weaknesses. IPv6 has become an essential technology for modern data centers, ISPs, and cloud computing. On the other hand, home networks with basic internet use and online gaming.
FAQ’s
Is ipv6 faster than ipv4?
Yes, IPV6 is faster than IPV4, offers greater address space, more bits, and strong security to the network.
Can you convert IPv4 to IPv6?
Yes, you can convert IPV4 to IPV6. There are three ways for the transition.
- You can create a dual StacK network.
- You can use IPV6 tunneling.
- You can use NAT protocol translation (NAT-PT).
Which is better, IPv4 or IPv6?
When comparing IPV4 vs IPV6, there is no doubt that IPV6 has an edge over its predecessor in terms of data integrity, a robust foundation, and overall security. IPV6 is faster than IPV4 and offers a more efficient and scalable network. While IPV4 can support mid-level gaming experiences, for high-end gaming experiences, you can get IPV6, as it offers faster and more reliable connections.
What happens if I change IPv4 to IPv6?
IPv6 offers built-in authentication and encryption directly into the IP layer. This creates a more secure data environment. It reduces complexity with SLAAC (Stateless Address Autoconfiguration), reduces data latency, and multicasting.
